How to Create a WordPress Website for Beginners: Complete Guide for 2025
Planning to kickstart your Startup, taking your business online or scaling your already established business? If you are here you might have already made up your mind to create a wordpress website but not sure on how to create a wordpress website?Did you know that over 43% of all websites on the internet are powered by WordPress? This statistic highlights WordPress’s strong presence in the website development field, demonstrating its flexibility and ease of use.
More than 61 million active websites, WordPress has cultivated a vibrant community of developers, designers, and content creators who contribute to its dynamic ecosystem. If you’re just starting with WordPress website development, you’re about to hop on an exciting journey that connects you with millions of users around the world. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll take you through everything you need to know to launch your WordPress journey, from installation to creating your first website.
Understanding WordPress: The Foundation of Modern Web Development

While there is no simple answer to how to create a WordPress Website? When starting create a wordpress website from a beginner’s perspective, it’s crucial to recognize that there are two versions of WordPress: WordPress.com and WordPress.org. You can think of WordPress.com as a fully furnished apartment—everything is set for you to move in, but your options for customization are quite limited. In contrast, WordPress.org resembles owning a house – it grants you full control over every detail, from the ground up.
The main difference between WordPress.com and WordPress.org is that .org offers more customization and monetization options. WordPress.com is a simple way to start for free, with the option to upgrade to paid plans as needed.
Many committed website developers favor WordPress.org, which is self-hosted, because of its extensive options for customization and expansion. This degree of versatility is precisely why leading companies like The New York Times, Sony Music, and Disney Blog choose WordPress to establish their online identity.
Why Choose WordPress?

1.User-Friendly Interface
So the question arises why businesses should invest in WordPress development? Although you have already figure it out but let us add more value to that.Well, one of the main reasons why WordPress is so popular among users of all experience levels and business sizes is its user-friendly and intuitive interface. People who are new to the platform find it easy to learn how to move around the dashboard.
They can quickly figure out how to create a WordPress Website, content and publish it for others to see. Additionally, users can personalize their websites to reflect their unique style and preferences even if they do not have any background in coding or web design. This accessibility makes WordPress a great choice for anyone looking to establish an online presence, whether for a personal blog, a business site, or an online portfolio.
2.Customization Options
Over 58000 plugins in the WordPress Plugin Directory, you can easily create a wordpress website and enhance your website’s features. There are plugins for improving search engine optimization, connecting to social media, and setting up e-commerce stores. You can also find plugins to create custom contact forms to engage visitors and gather information.
The WordPress ecosystem includes thousands of themes, from free to premium, allowing you to create a wordpress website and customize your site’s design easily. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced developer, many resources are available to help you tailor your WordPress site to your vision and needs.
3.Community Support
As a new WordPress user, you’ll find the community’s broad help invaluable. The official WordPress.org forums serve as a location for users to discuss their experiences, ask problems, and find solutions. You can get answers to frequent questions and connect with experienced users who are willing to help.
Furthermore, several online courses on platforms such as Udemy, Coursera, and LinkedIn Learning cater to all skill levels, including topics such as website design, plugin development, SEO, and e-commerce. These courses frequently give step-by-step instructions to help you grasp complicated ideas and to create a wordpress website.Many blogs, including WPBeginner and the official WordPress blog, provide insightful articles and tutorials to keep you current on trends and best practices.
Social media groups on platforms such as Facebook, Reddit, and LinkedIn promote community support by allowing users to share projects, solicit criticism, and cooperate. Participating in these groups can help inspire your own WordPress adventure and how to create a WordPress Website.
4.SEO-Friendly Features
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is essential for digital marketing since it improves your website’s exposure and accessibility. Optimizing your website can help you reach a broader audience, increase organic traffic, and generate conversions. WordPress is an excellent SEO platform with built-in best practices for search engine crawling and indexing.
It includes SEO-friendly features such as clean URL construction, tags, and categories, which enhance the user experience and site navigation. These characteristics increase engagement and indicate content relevance to search engines.
Consider using SEO plugins such as Yoast SEO or All in One SEO Pack. These tools include keyword analysis, readability tests, and automated XML sitemap development, making it easy to optimize your site without requiring substantial technical knowledge.According to research, WordPress sites frequently score higher in search engine results than sites built on other platforms due to their natural SEO skills.Box- “Complete Guide to Setting Up Yoast SEO on WordPress”
5.Regular Updates
A WordPress is a dynamic platform that is constantly evolving to create a wordpress website. Regular updates are required to improve security, defend websites from emerging threats, and ensure the confidentiality of sensitive information. These updates also include new features like themes and plugins, which allow users create a wordpress website and to customize their sites while improving performance.
User experience is a top emphasis, with engineers working to make the UI more intuitive for users of all skill levels. The WordPress dashboard makes it simple to manage updates, as users can apply updates with a single click, ensuring their sites have the most up-to-date features and security. In essence, WordPress’s dedication to regular upgrades improves both security and user experience.
Essential Tools for WordPress Website Development

Before diving into how to create a WordPress Website for beginners, you’ll need to gather your tools. Think of these as your digital toolbox:
Hosting and Domain
Your website needs a home (hosting) and an address (domain name). Consider starting with beginner-friendly hosts like Bluehost or SiteGround, which offer specialized WordPress hosting packages. Many of these hosts provide one-click WordPress installation, making the setup process incredibly smooth for beginners.
Theme Selection
Themes are like your website’s wardrobe – they determine how your site looks and feels. While WordPress comes with some basic themes, you might want to explore premium themes from reputable marketplaces. Remember, when starting WordPress website development for beginners, it’s better to choose a simple, lightweight theme that you can gradually customize rather than a complex one that might overwhelm you.
Getting Started: How to create a WordPress Website?

Starting your how create a wordpress website journey doesn’t have to be intimidating. Let’s break down the process in this detailed step by step guide on how to to create a wordpress website from scratch:
1. Installation and Setup
Method 1:How to Create a WordPress Website on Localhost
Step 1: Install Local Server Software
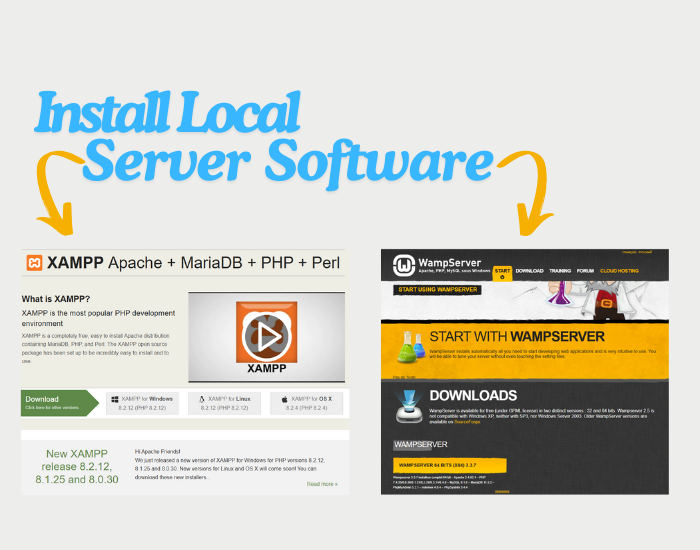
You need a local server environment (like XAMPP, WAMP, MAMP, or Local by Flywheel) that allows you to run WordPress on your computer.
- XAMPP: (Windows, Mac, Linux) – Download here
- WAMP: (Windows) – Download here
- MAMP: (Mac, Windows) – Download here
- Local by Flywheel: (Windows, Mac) – Download here
For this guide, we’ll use XAMPP:
- Download and install XAMPP.
- Once installed, open the XAMPP Control Panel and start Apache and MySQL.
Step 2: Download and Install WordPress
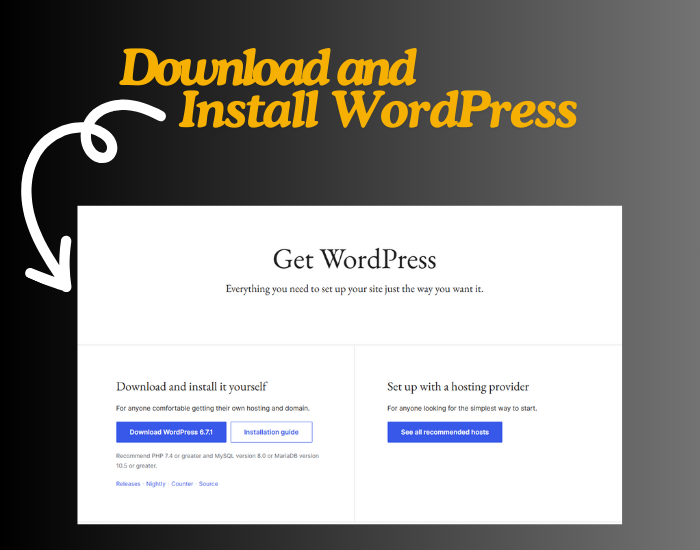
- Go to the WordPress.org website and download the latest version of WordPress.
- Extract the WordPress zip file.
- Move the extracted WordPress folder to the htdocs folder in your XAMPP directory (typically found in C:\xampp\htdocs on Windows).
Step 3: Create a Database for WordPress
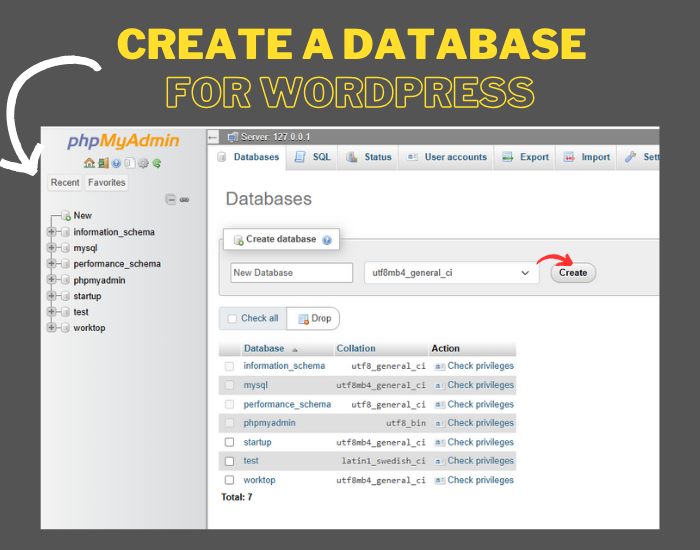
- Open your web browser and go to http://localhost/phpmyadmin.
- Click on the Databases tab.
- Create a new database by entering a name (e.g., wordpress_db) and clicking Create.
Step 4: Install WordPress Locally
1. In your browser, go to http://localhost/wordpress (or the name of the folder you moved to htdocs).
2. Choose your language and click Continue.
3. On the database setup screen, enter the following:
- Database Name: The name you created (e.g., wordpress_db).
- Username: root (default for local server).
- Password: Leave it blank (default for local server).
- Database Host: localhost.
- Table Prefix: wp_ (you can leave this as is or change it).
4. Click Submit and then click Run the installation.
5. Fill in your site information (site title, username, password, email) and click Install WordPress.
6. WordPress should now be installed, and you can log in to the admin dashboard at http://localhost/wordpress/wp-admin.
Method 2: How to Create a WordPress Website on Hosting (Live Server)
Step 1: Choose and Purchase a Hosting Plan

Choose a hosting provider that supports WordPress. Popular hosting providers include:
- Bluehost: bluehost.com
- SiteGround:siteground.com
- HostGator: hostgator.com
- Namecheap: namecheap.com
Most hosting providers offer one-click WordPress installation, but we’ll also cover manual installation.
Step 2: Choose and Register a Domain Name
You need a domain name for your website. You can purchase a domain from your hosting provider or a separate domain registrar like Namecheap.
Step 3: Install WordPress via Control Panel (cPanel)
Most hosting providers have cPanel with a one-click WordPress installation feature.
- Log in to cPanel (your hosting provider will give you access).
- Scroll down to the Softaculous App Installer or WordPress Installer.
- Click on WordPress and then click Install.
- Choose your domain from the dropdown menu.
- Set your site name, admin username, and password.
- Click Install and wait for the installation to complete.
- You can now access the WordPress dashboard at yourdomain.com/wp-admin.
Manual Installation (if one-click is not available):
1. Download WordPress from WordPress.org.
2. Upload WordPress Files:
- Use an FTP client, such as FileZilla, a common FTP client (download from here).
- Connect to your server using the FTP credentials provided by your hosting provider (usually something like ftp.yourdomain.com, with a username and password).
- Upload the extracted WordPress files to the public_html folder (or the folder specified by your host for website files).
3. Create a Database:
- In your hosting cPanel, go to the MySQL Databases section.
- Create a new database and name it (e.g., wordpress_db).
- Create a database user and assign it to the database (make sure to note the username, password, and database name).
4. Configure WordPress:
- Once the files are uploaded, visit yourdomain.com in your browser.
- You’ll be prompted to set up WordPress. On the database configuration page, enter:
- Database Name: The one you just created.
- Username: The database user you created.
- Password: The password for your database user.
- Database Host: This is usually localhost, but check with your hosting provider.
- Table Prefix: wp_ (or leave as is unless you want to change it).
- Click Submit and then Run the Installation.
5. Complete Installation:
- Set your site title, admin username, password, and email.
- Click Install WordPress.
- You can now log in to the WordPress dashboard by visiting yourdomain.com/wp-admin.
Common Steps After Installation (Applies to Both Localhost and Hosting)
Once WordPress is installed (either locally or on a live server), you can proceed with the following steps to build your website:
Step 1: Log in to the WordPress Dashboard
Access your WordPress dashboard:
- Localhost: Visit http://localhost/wordpress/wp-admin.
- Hosting: Visit yourdomain.com/wp-admin.
Step 2: Choose and Install a Theme
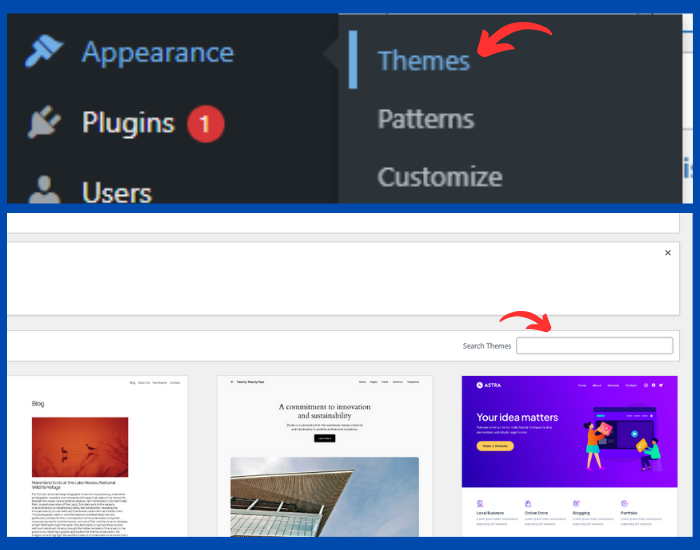
- Go to Appearance > Themes in the WordPress dashboard.
- Click Add New and browse the available themes, or search for a specific theme.
- Choose a theme you like and click Install.
- After installation, click Activate to apply the theme to your website.
- Alternatively, you can purchase a premium theme from providers like ThemeForest or Elegant Themes, then upload it by clicking Upload Theme in the Themes section.
Step 3: Install Essential Plugins
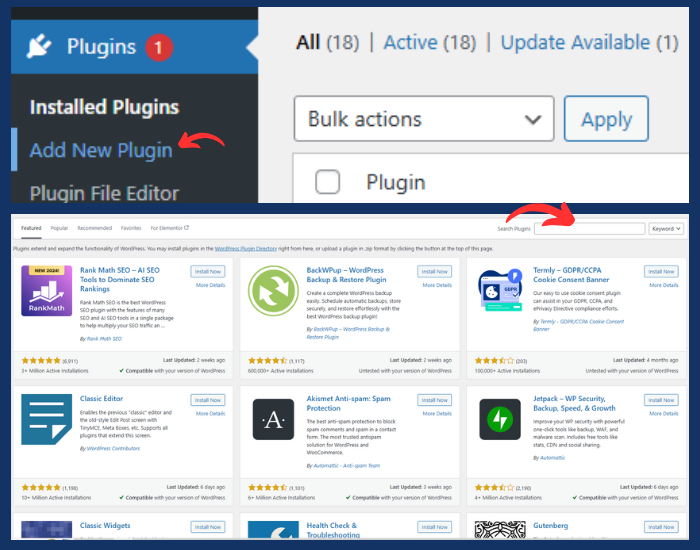
Plugins extend the functionality of your WordPress site. You can install plugins from Plugins > Add New. Below are some essential plugins:
- SEO: Install Yoast SEO or Rank Math to optimize your site for search engines.
- Security: Install Wordfence or Sucuri for security.
- Caching: Install W3 Total Cache or WP Super Cache to improve your site’s speed.
- Contact Form: Install Contact Form 7 or WPForms.
- Backup: Install UpdraftPlus to create backups of your site.
Step 4: Customize Your Website
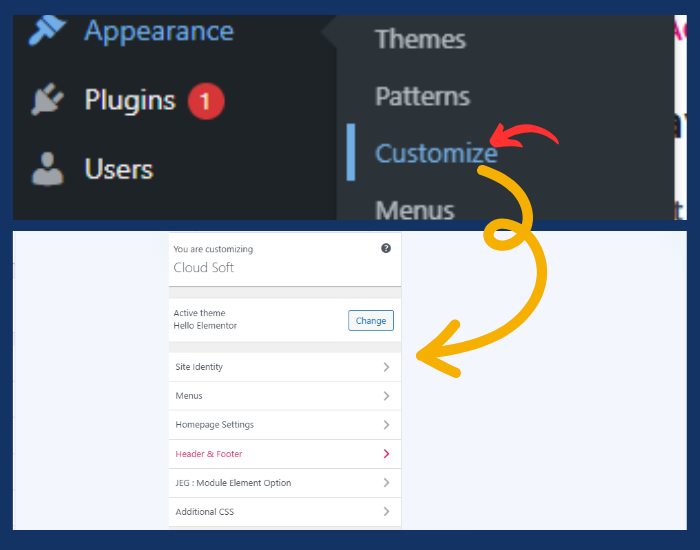
Go to Appearance > Customize to access the WordPress Customizer. Here you can:
- Change the site title and tagline.
- Upload a logo and favicon.
- Configure your homepage settings (choose between displaying your latest posts or a static page).
- Modify the color scheme and fonts.
Step 5: Create Important Pages (Continued)
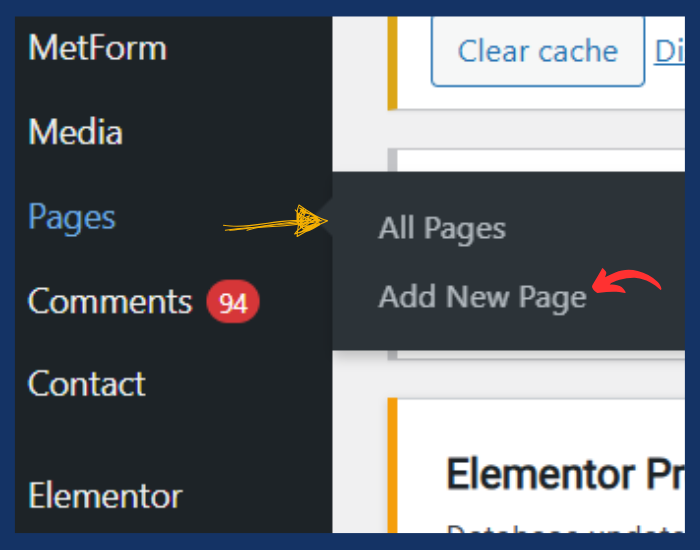
1.Go to Pages > Add New to create essential pages like:
- Home: This will be the main landing page of your website.
- About: Provide information about your business, blog, or personal background.
- Services: If applicable, list the services you offer.
- Contact: Use a contact form plugin (e.g., WPForms or Contact Form 7) to create a form for visitors to contact you. Include your address, phone number, and/or social media links if needed.
- Blog: If your website is a blog or includes a blog section, create a dedicated page for your blog posts.
- After creating each page, ensure they are published by clicking the Publish button on the right-hand side of the page editor.
Step 6: Set Up Your Menu
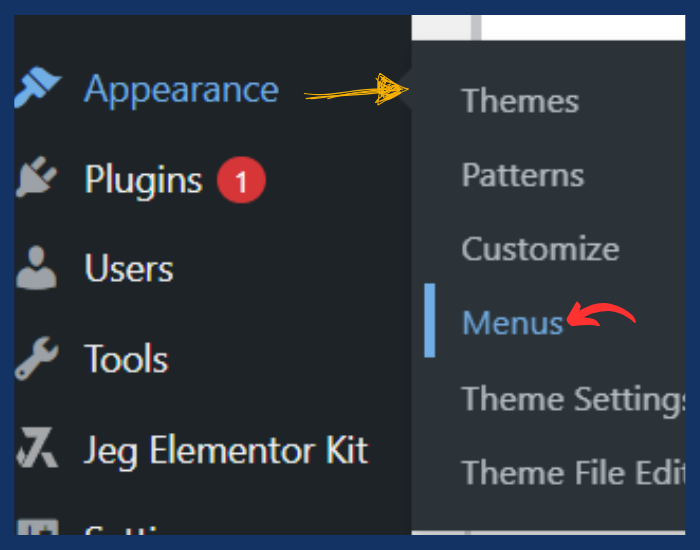
To make your site easy to navigate, you should set up a menu.
- Go to Appearance > Menus.
- Enter a name for your menu (e.g., “Main Menu”) and click Create Menu.
- On the left side, you’ll see a list of pages, posts, and categories. Select the pages you want to include in your menu (e.g., Home, About, Contact) and click Add to Menu.
- 4. Drag and drop the menu items to arrange them in the order you prefer.
- 5. Under Menu Settings, select Primary Menu (or the appropriate location, depending on your theme) to ensure it appears in the correct position on your website.
- Click Save Menu.
Step 7: Configure Your Homepage
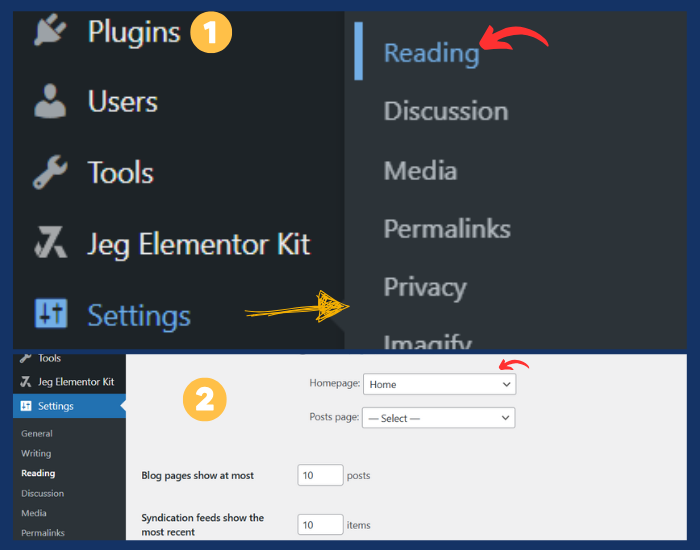
By default, WordPress displays your latest posts on the homepage, but you can change this to a static page if you want a custom homepage.
- Go to Settings > Reading.
- Under Your homepage displays, select A static page.
- Set the Homepage to the page you created (e.g., “Home”) and the Posts page to your blog page (if applicable).
- Click Save Changes.
Step 8: Customize Permalinks (URL Structure)
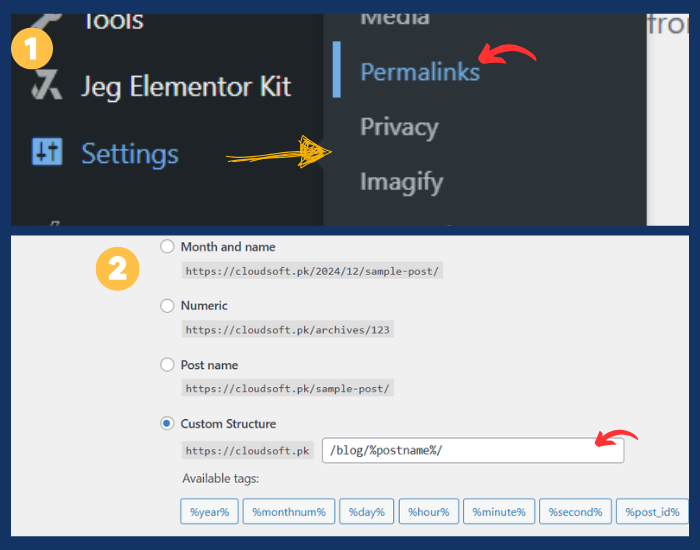
For SEO purposes and to make your URLs more user-friendly, change the permalink structure.
- Go to Settings > Permalinks.
- Choose the Post name option to make your URLs based on the title of your posts/pages (e.g., yourdomain.com/sample-page).
- Click Save Changes.
Step 9: Add Content
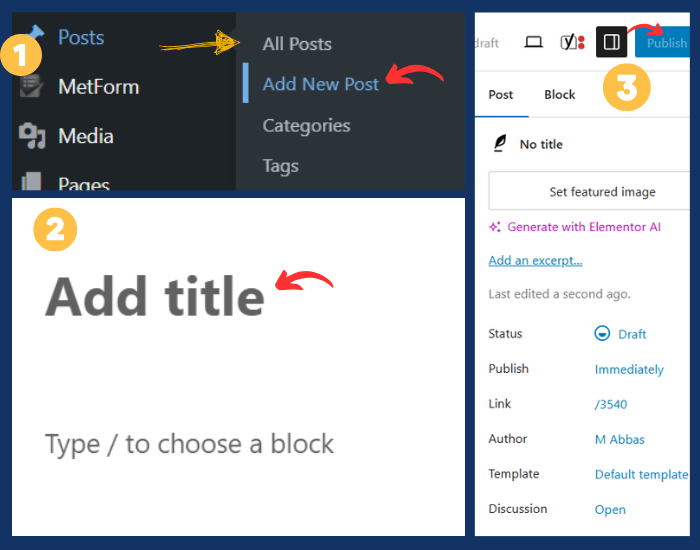
Now that the site structure is in place, it’s time to add content:
- Posts: If you’re running a blog, create blog posts by going to Posts > Add New.
- Enter a title and content for your post.
- Use the Gutenberg block editor to add images, paragraphs, headings, lists, etc.
- Assign categories and tags to organize your blog content.
- Click Publish when you’re ready to post.
2. Pages: Continue to add content to your static pages (e.g., About, Services, Contact) by going to Pages > All Pages and editing the respective pages.
Step 10: Add Widgets (Optional)
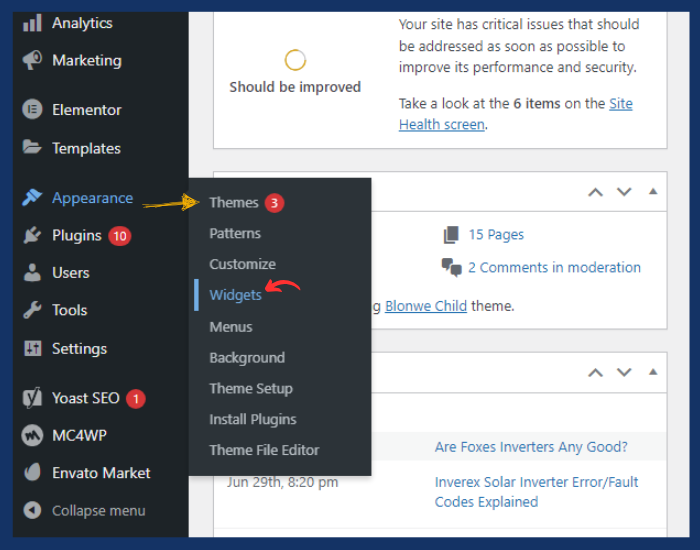
Widgets are small content blocks that can be added to specific areas of your site, such as the sidebar or footer.
- Go to Appearance > Widgets.
- Depending on your theme, you’ll see widget areas like Sidebar, Footer, etc.
- You can drag and drop widgets (e.g., Recent Posts, Search, Social Media Links) into these areas.
- Customize each widget’s settings as per your needs.
Step 11: Test Your Website
Before launching your website, you should thoroughly test it to ensure everything works properly.
- Check Responsiveness: Use your browser’s developer tools (F12 key or right-click and choose Inspect) to view your website on different screen sizes (mobile, tablet, desktop).
- Check Links and Forms: Ensure all menus, links, and contact forms are functioning correctly.
- Browser Compatibility: Test your website on different browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge) to ensure compatibility.
- Performance Testing: Use tools like GTmetrix or Google PageSpeed Insights to check your website’s performance and load times.
Step 12: Optimize for SEO
To ensure your website performs well in search engines, implement basic SEO practices:
1. SEO Plugin Setup: If you installed an SEO plugin like Yoast SEO or Rank Math, configure it for optimal performance:
- Yoast SEO: Go to SEO > General and follow the configuration wizard.
- Rank Math: Go to Rank Math > Dashboard and run the setup wizard.
2. Set Meta Titles and Descriptions:
- For each page and post, scroll down to the SEO section (provided by Yoast or Rank Math) and add a custom meta title and meta description. These are the titles and snippets that appear in search engine results
3. Submit XML Sitemap to Google Search Console:
- Both Yoast and Rank Math generate a sitemap for you (e.g., yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml).
- Go to Google Search Console and submit your website to track its performance in Google. Submit the sitemap link to help Google index your site faster.
4. Use Keywords:
- Research keywords related to your niche using tools like Google Keyword Planner or Ubersuggest.
- Integrate these keywords naturally into your content, headings, and meta tags.
5. Optimize Images:
- Use an image compression plugin like Smush or Imagify to reduce the file size of images without losing quality.
- Add alt text to all images, describing what the image is about. This helps with SEO and accessibility.
6. Internal Linking:
- As you add content to your website, make sure to create internal links between pages and posts. This helps improve SEO by showing search engines the structure of your website.
Step 13: Secure Your Website
Security is essential to protect your website from hackers and malware.
1. Install a Security Plugin:
- Use Wordfence or Sucuri Security to enhance your website’s protection.
- After installation, follow the plugin’s setup guide to scan your site for vulnerabilities and configure firewall settings.
2. Enable SSL (HTTPS):
- Most hosting providers offer free SSL certificates (via Let’s Encrypt). SSL encrypts the data transferred between your site and its visitors, making it more secure.
- In cPanel, look for the SSL/TLS Manager and activate your SSL certificate for your domain.
After enabling SSL, go to Settings > General in WordPress and update WordPress Address (URL) and Site Address (URL) to use https:// instead of http://.
3. Limit Login Attempts:
- To prevent brute force attacks, limit the number of login attempts with a plugin like Limit Login Attempts Reloaded.
4. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA):
- Use a plugin like Two Factor Authentication to add an extra layer of security for logging in.
5. Change Default Admin Username:
- If you haven’t already, avoid using “admin” as your username. Create a new user with a stronger username and assign it administrator privileges, then delete the old “admin” user.
Step 14: Set Up Backups
Regular backups are critical in case something goes wrong with your website.
1. Install a Backup Plugin:
- Use UpdraftPlus (free) or BackupBuddy (premium) to schedule automatic backups of your WordPress site.
- UpdraftPlus Setup:
- Go to Settings > UpdraftPlus Backups.
- Choose how often you want to back up your files and database (e.g., weekly).
- Set up remote storage (e.g., Google Drive, Dropbox) to store your backups off-site.
- Click Backup Now to create your first backup.
2. Test Your Backup:
- After creating a backup, simulate a restore process to ensure everything works properly.
Step 15: Test Your Website Again Before Launch
Before launching your website for the world to see, perform a final round of testing:
Step 15: Test Your Website Again Before Launch
- Ensure that your website looks good and functions properly on mobile devices. You can use tools like Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to verify this.
Step 15: Test Your Website Again Before Launch
2. Test All Forms:
- Ensure that all contact forms, subscription forms, and any other interactive elements are working correctly and delivering data as expected.
3. Check for Broken Links:
- Use a plugin like Broken Link Checker to scan your website for any broken links that could hurt user experience or SEO.
4. Browser Testing:
- Test your website on different browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge) to ensure compatibility across all platforms.
- You can use tools like BrowserStack to test your site on various browsers and devices without needing to install them.
5. Performance Testing:
- Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix to check your website’s performance and speed.
- These tools will give you recommendations to improve your site’s loading time, such as enabling caching, compressing images, and minimizing CSS/JavaScript.
6. Check SEO Readiness:
- Ensure that all your pages and posts have proper meta titles and meta descriptions.
- Verify that your XML sitemap has been successfully submitted to Google Search Console and that no errors are reported.
- Use the Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools to monitor for SEO issues.
Step 16: Optimize Website Speed
Website speed is crucial for user experience and SEO. Here’s how to optimize it:
1. Caching:
- Install a caching plugin like W3 Total Cache or WP Super Cache.
- These plugins store static versions of your pages, which reduces the load time for visitors.
2. Minify CSS and JavaScript:
- Use plugins like Autoptimize or W3 Total Cache to minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML files.
- This reduces file sizes and improves loading times.
3. Optimize Images:
- If you haven’t already, install Smush or Imagify to compress images without sacrificing quality.
- Ensure that your images are in the correct format (WebP is preferred for web images) to further reduce load times.
4. Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN):
- A CDN stores copies of your site on multiple servers around the world, delivering your content more quickly to visitors based on their location.
- Popular CDN providers include Cloudflare (which offers a free plan) and KeyCDN.
5. Lazy Loading:
- Enable lazy loading to defer the loading of images and videos until they are actually needed, which improves initial page load times.
- WordPress 5.5 and later has built-in lazy loading, but you can also use plugins like Lazy Load by WP Rocket.
Step 17: Launch Your Website
1.Remove Maintenance Mode:
- If you used a maintenance mode plugin during development, go to Settings > Maintenance Mode (or your specific plugin’s settings) to disable it.
- Ensure that your entire website is accessible to the public.
2. Submit Your Website to Search Engines:
- If you haven’t already, submit your website to search engines.
- Google: Use Google Search Console to submit your URL for indexing.
- Bing: Use Bing Webmaster Tools to submit your site to Bing.
3. Announce Your Launch:
- Share your website launch on social media, by email, and with any other marketing methods you have planned.
- If you have an email list, send a newsletter to let your subscribers know the site is live.
4. Monitor Your Traffic:
- Install Google Analytics to track visitors, page views, bounce rates, and more.
- You can set up Google Analytics by installing the MonsterInsights plugin or adding the Google Analytics tracking code manually.
5. Monitor Site Errors:
- Use Google Search Console to monitor for any crawl errors or issues with your site.
- Regularly check for any errors that could affect SEO, such as broken links or indexing problems.
Step 18: Regular Maintenance
Maintaining your WordPress website is critical to ensure its security, performance, and functionality over time.
1. Regular Updates:
- Go to Dashboard > Updates to check for updates to WordPress core, themes, and plugins.
- Always update your WordPress installation, themes, and plugins to the latest versions to prevent vulnerabilities.
2. Backup Your Website:
- Ensure your backup schedule is working properly (using UpdraftPlus or another backup plugin).
- Regularly download copies of your backups and store them off-site (e.g., on Google Drive or Dropbox).
3. Security Monitoring:
- Keep an eye on your security plugin (e.g., Wordfence or Sucuri) for any alerts or issues.
- Regularly scan for malware and review security logs.
- Consider setting up email notifications for any suspicious activity, such as failed login attempts or changes to core files.
4. Database Optimization:
- Over time, your WordPress database can accumulate unnecessary data (such as post revisions, spam comments, and trash).
- Use a plugin like WP-Optimize or Advanced Database Cleaner to clean up your database and improve performance.
5. Check for Broken Links:
- Use Broken Link Checker periodically to scan for broken or dead links.
- Remove or update any broken links to ensure a smooth user experience and maintain SEO rankings.
6. Test Website Performance:
- Regularly run performance tests using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTMetrix, or Pingdom to ensure your website continues to load quickly.
- If performance starts to lag, review caching settings, image optimization, and consider upgrading your hosting plan if necessary.
7. Review SEO:
- Periodically audit your site’s SEO performance:
- Use Google Search Console to identify issues like crawl errors, indexing problems, or mobile usability issues.
- Use an SEO plugin like Yoast SEO or Rank Math to analyze the SEO of individual pages and posts.
- Update old posts with fresh content and keywords to keep them relevant and maintain or improve their search rankings.
8. Test Functionality After Updates:
- After updating WordPress core, themes, or plugins, test your website’s functionality:
- Make sure forms are working correctly.
- Ensure that the design and layout haven’t been affected.
- Check for broken elements, especially if you’re using custom code or third-party plugins.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Step 19: Grow Your Website
Now that your website is live and maintained regularly, you can focus on growing your presence and audience.
1. Content Strategy:
- Develop a regular content schedule. If your site includes a blog, aim to publish new posts consistently to engage visitors and improve SEO.
- Focus on creating high-quality, valuable content that addresses your audience’s needs and questions.
- Use tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, or Ubersuggest to identify new content opportunities and keyword ideas.
2. Social Media Integration:
- Promote your content on social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and LinkedIn.
- Use a plugin like Social Snap or Shared Counts to add social sharing buttons to your blog posts and pages, making it easy for visitors to share your content.
3. Email Marketing:
- Build an email list using an email marketing service like Mailchimp, ConvertKit, or Sendinblue.
- Use a plugin like Mailchimp for WordPress or Newsletter to integrate signup forms on your website.
- Send newsletters to your subscribers with updates, blog posts, promotions, and more to keep them engaged.
4. Monetize Your Website (If Applicable):
- If you’re looking to monetize your website, explore options like:
- Ad Networks: Sign up for Google AdSense or Media.net to display ads on your website.
- Affiliate Marketing: Join affiliate programs (e.g., Amazon Associates, ShareASale) and promote products or services to earn commissions.
- E-commerce: If applicable, set up an online store using WooCommerce to sell products or services.
5. Analytics and Goal Tracking:
- Regularly check Google Analytics to understand your audience’s behavior, track traffic sources, and monitor conversions.
- Set up specific goals in Google Analytics (e.g., form submissions, purchases, newsletter signups) to track the success of your website’s objectives.
6. Engage with Your Audience:
- Respond to comments on your blog posts and engage with your followers on social media.
- Consider adding a live chat feature using plugins like Tawk.To or LiveChat to provide real-time support or interaction with visitors.
7. Create Backup Strategies for Major Changes:
- Before making significant changes to your website (such as design overhauls, new plugins, or theme updates), create a fresh backup.
- Test major changes in a staging environment (many hosting providers offer this feature) to ensure they won’t break the live site.
8. Optimize for Accessibility:
- Ensuring your website is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities, is not only good for user experience but also improves SEO and can help you avoid legal issues.
- Here are key steps to improve accessibility:
- Use descriptive alt text for all images, so screen readers can describe the image to visually impaired users.
- Ensure high contrast between text and background colors to make content easier to read.
- Add captions to videos and transcripts for audio content.
- Use proper HTML tags for headings (e.g., <h1>, <h2>, etc.) so that screen readers can navigate the content easily.
- Test for Accessibility: Use tools such as WAVE Web Accessibility Tool or Lighthouse to identify areas where your site could be improved for accessibility.
9. Optimize for Mobile:
- Since a significant portion of web traffic comes from mobile devices, ensuring your site is fully responsive is crucial.
- Test mobile responsiveness using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test and make sure all elements are easily navigable, readable, and functional on smaller screens.
- Use responsive themes and test all forms, buttons, and images to ensure they are optimized for mobile devices.
- Consider AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages) for faster loading times on mobile devices. You can use the AMP plugin for WordPress to implement this.
10. Enable Structured Data (Schema Markup):
- Schema markup helps search engines understand the structure of your website’s content and can enhance your appearance in search results by adding rich snippets (e.g., star ratings, event times, product information).
- Use a plugin like Schema Pro or Yoast SEO (which includes basic schema support) to implement structured data for things like:
- Blog articles
- Products
- Events
- Reviews
- You can test your structured data using Google’s Rich Results Test.
11. Regularly Audit Your Website:
- Websites can accumulate technical issues over time, such as slow loading pages, broken links, or outdated content. It’s important to perform regular audits to ensure your site is running optimally.
- SEO Audit: Use SEMrush or Ahrefs to perform an SEO audit and identify any issues with broken links, duplicate content, or missing meta descriptions.
- Speed Audit: Regularly check your website’s speed using GTMetrix or Google PageSpeed Insights and address any issues that may slow down your site.
- Content Audit: Review your blog posts, pages, and media files periodically to ensure all content is up to date, relevant, and optimized for SEO.
Step 20: Advanced Strategies for Long-Term Growth
Implement A/B Testing:
- A/B testing (also known as split testing) helps you determine which version of a page or element performs better.
- Tools like Google Optimize or Optimizely allow you to create and test different variations of your website (e.g., different headlines, button colors, layouts) to see which one leads to higher conversions or engagement.
2. Set Up E-commerce (If Applicable):
- If you plan to sell products or services, consider setting up an online store using WooCommerce (the most popular WordPress e-commerce plugin).
- WooCommerce Setup:
- Install the WooCommerce plugin from the WordPress plugin repository.
- Follow the setup wizard to configure your store, including payment gateways (like PayPal, Stripe), shipping options, and tax settings.
- Add product listings with detailed descriptions, pricing, and images.
- Make sure to optimize your product pages for SEO by using keywords in product titles, descriptions, and alt text for images.
3. Integrate Memberships or Subscription-Based Content:
- If you want to offer exclusive content or services, consider adding a membership system to your website.
- Use plugins like MemberPress or Restrict Content Pro to create membership levels, gated content, and subscription plans.
- This business model is ideal for websites offering premium content (e.g., online courses, e-books, or exclusive blog posts).
4. Create an Online Course (If Applicable):
- If your website is focused on education, training, or offering specialized knowledge, creating an online course can be a highly effective way to engage your audience and monetize your expertise.
- Use a Learning Management System (LMS) plugin like LearnDash or LifterLMS to build and manage your courses.
Steps to Set Up an Online Course:
- install the LMS Plugin: Install LearnDash, LifterLMS, or a similar plugin that is compatible with WordPress.
- Create Course Content:
- Divide your course into modules and lessons.
- Add multimedia content like videos, downloadable PDFs, quizzes, and assignments to make the course interactive.
- Set Pricing: Define whether your course will be free or paid. If paid, configure pricing plans (one-time payment or subscription-based).
- Enable User Registration: Allow users to create accounts to access the course. This can be integrated with a membership plugin or handled via the LMS plugin.
- Promote Your Course: Use email marketing, social media, and SEO tactics to promote your course to your target audience.
Improve User Engagement:
- User engagement is key to building a loyal audience and keeping visitors on your site longer. Here are some ways to enhance engagement:
Encourage Comments and Discussions:
- Enable Comments: Allow readers to comment on your blog posts and content. Use a plugin like Disqus or the built-in WordPress comments system.
- Moderate Comments: Regularly interact with users by replying to their comments and fostering discussions. This helps build community and trust.
Add Social Sharing Buttons:
- Install a plugin like Social Snap or Monarch to add social media share buttons to your posts and pages. This encourages readers to share your content, increasing its reach.
Use Pop-Ups and Notifications:
- Use tools like OptinMonster or Sumo to create targeted pop-ups that promote lead magnets, email signups, or special offers.
- Push Notifications: Add push notifications using a service like OneSignal to notify users of new blog posts, updates, or offers.
Surveys and Polls:
- Engage your visitors with interactive elements such as surveys or polls. Use plugins like WPForms or YOP Poll to gather feedback and insights from your audience.
Optimize for Conversions:
- If your website’s goal is to generate leads, sales, or signups, focus on Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO).
Add Clear Calls to Action (CTAs):
- Strategically place CTAs on your homepage, blog posts, and landing pages to encourage users to take action (e.g., sign up for a newsletter, purchase a product, or contact you).
- Use buttons with contrasting colors and action-oriented text like “Get Started” or “Sign Up Now.”
Create Dedicated Landing Pages:
- Use a landing page builder like Elementor or SeedProd to create high-converting landing pages for specific campaigns (e.g., product launches, lead magnets).
- Ensure these pages have a single focus and minimal distractions (e.g., no navigation menu) to increase conversions.
Use A/B Testing:
- Test different headlines, page layouts, CTAs, and images using Google Optimize or Optimizely to see what resonates best with your audience.
- Continuously optimize your website based on data-driven insights to improve conversion rates.
Build an Email List:
- Email marketing is one of the most effective ways to retain and engage users. Building an email list allows you to nurture relationships with your audience and drive repeat traffic to your site.
Steps to Build an Email List:
- Choose an Email Marketing Service: Use platforms like Mailchimp, ConvertKit, or Sendinblue to manage your email campaigns.
- Create Opt-in Forms: Use plugins like Mailchimp for WordPress or Thrive Leads to add email signup forms to your site.
- Offer a Lead Magnet: Encourage visitors to sign up by offering a free resource (e.g., eBook, template, or discount) in exchange for their email address.
- Segment Your List: Organize your email list into segments (e.g., new subscribers, engaged users, buyers) to send targeted emails.
- Send Regular Newsletters: Keep your audience engaged by sending newsletters with updates, blog posts, and promotions.
Here's a summary of the overall process:
WordPress Setup:
- Localhost: Install XAMPP, MAMP, or another local server, set up a database, and install WordPress locally to test and develop your site.
- Live Hosting: Choose a hosting provider, register a domain, and install WordPress either via cPanel (one-click install) or manually using FTP and database setup.
Website Design and Structure:
- Choose and install a theme that fits your website’s goals.
- Install essential plugins (SEO, security, caching, backups) to extend the functionality of your site.
- Set up menus, create important pages (Home, About, Blog, Contact), and configure permalinks for clean URLs.
Content Creation and Engagement:
- Add content to your pages and blog. Ensure the content is optimized for SEO with relevant keywords, meta tags, and internal links.
- Engage visitors with comments, social sharing buttons, and interactive elements such as forms and pop-ups.
Optimization:
- Improve site speed with caching, image optimization, and possibly using a CDN.
- Ensure your website is mobile-friendly and accessible, following best practices for web design and user experience.
- Regularly audit your site for broken links, SEO issues, and performance bottlenecks.
Security and Maintenance:
- Protect your website with security plugins, SSL certificates, and regular backups.
- Update WordPress, themes, and plugins to prevent vulnerabilities.
- Clean your database periodically and monitor potential security threats.
Advanced Growth Strategies:
- Implement strategies like A/B testing, conversion rate optimization (CRO), email marketing, and social media integration to scale your website.
- Consider adding e-commerce with WooCommerce, offering online courses, or creating a membership system to diversify your revenue streams.
Long-Term Website Management:
- Engage with your audience through email newsletters, blog posts, and social media.
- Continuously improve your site based on user feedback, analytics data, and performance testing.
- Keep your website relevant and fresh by regularly updating content and design elements.
By following these detailed steps, you can create a fully functional, secure, and optimized WordPress website that is ready to grow and succeed over time. Whether you’re building a personal blog, business website, or e-commerce site, the flexibility of WordPress makes it possible to bring your vision to life. Just remember that maintaining and growing your website is an ongoing process—regular updates, fresh content, and continued optimization will keep your website thriving for years to come.
Your Website is Your Digital Front Door – Make it Count!
At CloudSoft, we’re not just building websites, we’re building solutions that help you achieve your business goals. Whether you need a sleek, professional portfolio, a robust e-commerce platform, or a fully customized solution, we’re here to turn your vision into reality.
Let’s transform your digital presence! Contact CloudSoft today, and let’s build a WordPress website that works as hard as you do
Why Choose CloudSoft for Your WordPress Website Development?
- Custom Design: No cookie-cutter templates here! We design websites that reflect your brand’s personality, ensuring a unique and engaging user experience.
- Speed and Performance: Slow-loading websites lose customers. Our team ensures that your site is optimized for speed, keeping your visitors engaged and boosting your SEO rankings.
- SEO-Optimized: We build every website with SEO best practices in mind, helping your business rank higher in search engines and attract more organic traffic.
- Mobile-First Approach: With more users browsing on mobile, we ensure your website is fully responsive and looks great on every device—whether it’s a smartphone, tablet, or desktop.
- Security You Can Trust: Your website’s security is our priority. We implement the latest security measures, including SSL certificates, firewalls, and regular updates, to keep your site safe from threats.
- Scalability and Flexibility: As your business grows, so will your website. WordPress offers limitless possibilities for adding new features, integrating e-commerce, or creating membership sites, and CloudSoft will be with you every step of the way.
- Dedicated Support: We don’t just build websites and walk away. Our team provides ongoing support and maintenance to ensure your site continues to perform at its best.
Whether you’re building a personal blog or a business website, the information you learned here on how to create a website on WordPress will serve as a foundation for your WordPress website development future. Start small, be patient, and remember that the WordPress community is always here to help.
Need professional guidance on your WordPress journey? Our team of experienced developers specializes in helping beginners create stunning WordPress websites. Contact us for a free consultation and let’s bring your vision to life!
If you feel like you missed something or want to revisit a topic, here’s a summary of the overall process. Click to revisit the section:
- WordPress Setup:
- Localhost: Install XAMPP, MAMP, or another local server, set up a database, and install WordPress locally to test and develop your site.
- Live Hosting: Choose a hosting provider, register a domain, and install WordPress either via cPanel (one-click install) or manually using FTP and database setup.
2. Website Design and Structure:
- Choose and install a theme that fits your website’s goals.
- Install essential plugins (SEO, security, caching, backups) to extend the functionality of your site.
- Set up menus, create important pages (Home, About, Blog, Contact), and configure permalinks for clean URLs.
3. Content Creation and Engagement:
- Add content to your pages and blog. Ensure the content is optimized for SEO with relevant keywords, meta tags, and internal links.
- Engage visitors with comments, social sharing buttons, and interactive elements such as forms and pop-ups.
4. Optimization:
- Improve site speed with caching, image optimization, and possibly using a CDN.
- Ensure your website is mobile-friendly and accessible, following best practices for web design and user experience.
- Regularly audit your site for broken links, SEO issues, and performance bottlenecks.
5. Security and Maintenance:
- Protect your website with security plugins, SSL certificates, and regular backups.
- Update WordPress, themes, and plugins to prevent vulnerabilities.
- Clean your database periodically and monitor potential security threats.
6. Advanced Growth Strategies:
- Implement strategies like A/B testing, conversion rate optimization (CRO), email marketing, and social media integration to scale your website.
- Consider adding e-commerce with WooCommerce, offering online courses, or creating a membership system to diversify your revenue streams.
7. Long-Term Website Management:
- Engage with your audience through email newsletters, blog posts, and social media.
- Continuously improve your site based on user feedback, analytics data, and performance testing.
- Keep your website relevant and fresh by regularly updating content and design elements.
Table of Contents
Dont Hesitate To Contact Us
Make Contact With Us & Get Best & Cheap Digital Solutions. Get Started Now & Boost Your Online Presence.
